Stainless steel furnace tubes are critical components in industries that operate under extreme heat and corrosive environments. These tubes ensure efficient heat transfer, structural integrity, and longevity in systems ranging from chemical processing to power generation. In this blog, we delve into what stainless steel furnace tubes are, their types, standout features, and the diverse applications that rely on their performance.
What is a Stainless Steel Furnace Tube?
A stainless steel furnace tube is a cylindrical component designed to withstand high temperatures, pressure, and corrosive conditions within industrial furnaces and heating systems. Made from austenitic or ferritic stainless steel grades, these tubes facilitate the transfer of heat, gases, or fluids while maintaining structural stability. Their ability to resist oxidation, scaling, and thermal fatigue makes them indispensable in demanding environments.
Industries use stainless steel furnace tubes in boilers, heat exchangers, reactors, and pyrolysis units. Their versatility stems from stainless steel’s unique properties, including exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal efficiency.
Types of Stainless Steel Furnace Tubes
Stainless steel furnace tubes are categorized based on material grade, design, and application requirements. Below are the primary types:
1. Austenitic Stainless Steel Tubes (Grades 304, 316, 310)
- Grade 304: Offers excellent corrosion resistance and durability for general-purpose furnace applications.
- Grade 316: Contains molybdenum for enhanced resistance to chlorides and acidic environments. Ideal for chemical processing.
- Grade 310: Designed for extreme heat (up to 1150°C), making it suitable for high-temperature furnaces and kilns.
2. Ferritic Stainless Steel Tubes (Grade 430, 446)
- Grade 430: Cost-effective with moderate heat and corrosion resistance. Used in mildly corrosive environments.
- Grade 446: Contains chromium for superior oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures.
3. U-Shaped and Straight Tubes
- U-Shaped Tubes: Ideal for thermal expansion management in heat exchangers and boilers.
- Straight Tubes: Used in applications requiring uniform heat distribution, such as radiant sections of furnaces.
4. Coiled Tubes
Compact helical designs maximize surface area for heat transfer in confined spaces, common in pyrolysis and reforming units.
Key Features of Stainless Steel Furnace Tubes
The performance of stainless steel furnace tubes hinges on their material and engineering properties. Here are their defining features:
1. High-Temperature Resistance
Stainless steel retains strength and resists deformation at temperatures exceeding 1000°C, ensuring reliability in furnaces and reactors.
2. Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Chromium content (10–30%) forms a passive oxide layer, protecting against rust, acids, and sulfidation in harsh environments.
3. Thermal Conductivity
Efficient heat transfer minimizes energy waste, optimizing furnace efficiency.
4. Mechanical Strength
Withstands internal pressure, thermal cycling, and mechanical stress without cracking or warping.
5. Low Maintenance
Resistance to scaling and chemical degradation reduces downtime for cleaning or replacements.
Applications of Stainless Steel Furnace Tubes
Industries worldwide rely on stainless steel furnace tubes for critical thermal processes. Key applications include:
1. Petrochemical and Refining
- Cracking Furnaces: Tubes transport hydrocarbons at high temperatures to break down complex molecules.
- Reformers: Facilitate hydrogen production and sulfur removal in refineries.
2. Power Generation
- Boilers and Superheaters: Convert water to steam for turbine-driven electricity generation.
- Heat Recovery Steam Generators (HRSGs): Capture waste heat in combined-cycle power plants.
3. Chemical Processing
- Reactors: Enable controlled reactions under high heat and pressure.
- Distillation Columns: Separate chemical compounds using thermal gradients.
4. Heat Treatment Furnaces
Used in annealing, hardening, and tempering metals to enhance mechanical properties.
5. Renewable Energy
- Solar Thermal Systems: Transfer heat from concentrated solar power (CSP) installations.
- Biomass Plants: Handle high-temperature gases during biofuel production
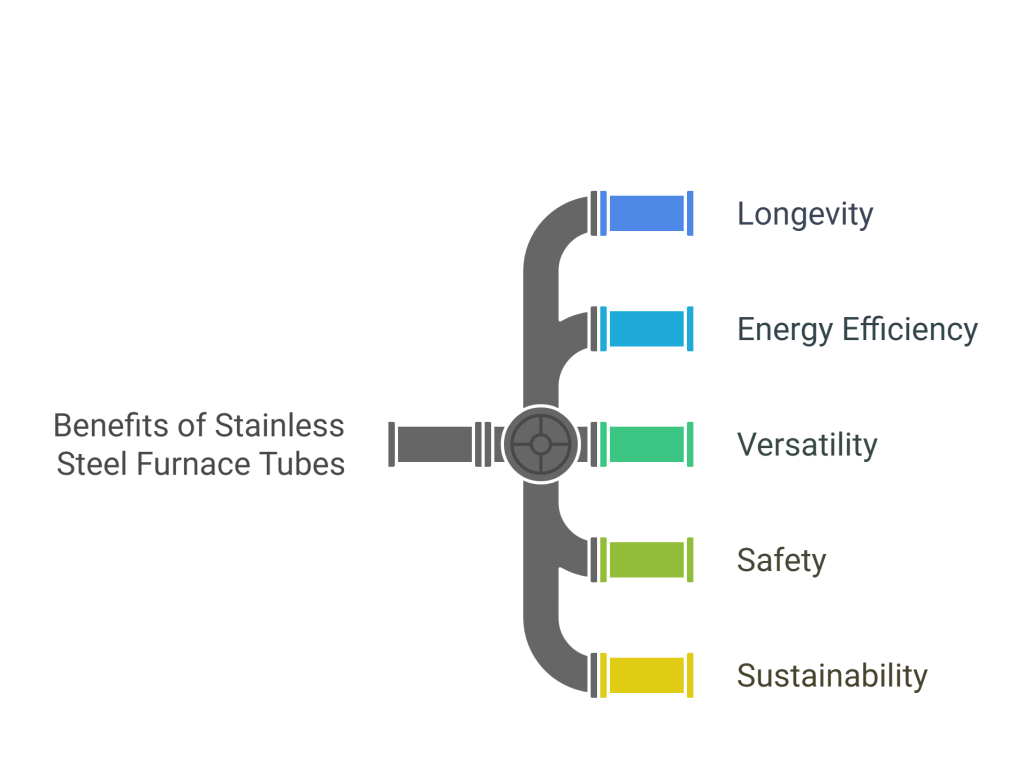
Advantages of Stainless Steel Furnace Tubes
Selecting the Right Stainless Steel Furnace Tube
When choosing a furnace tube, consider these factors:
- Operating Temperature: Match the steel grade (e.g., Grade 310 for ultra-high temperatures).
- Environment: opt for molybdenum-rich grades (316) in chloride-rich settings.
- Pressure Requirements: Ensure wall thickness and diameter meet system demands.
- Manufacturer Expertise: Partner with suppliers who adhere to ASTM/ASME standards and offer custom solutions.
Conclusion
Stainless steel furnace tubes are the backbone of industrial heating systems, offering unmatched durability, efficiency, and adaptability. From petrochemical plants to renewable energy facilities, their ability to thrive under extreme conditions ensures seamless operations and cost savings. By understanding the types, features, and applications of these tubes, industries can make informed decisions that enhance performance and sustainability.